Overview of Telemedicine Technologies
The realm of telemedicine solutions has seen a transformative shift, particularly within rural healthcare technology. As technology advances, mobile health apps and platforms are becoming indispensable in providing patient care. Mobile health apps facilitate remote monitoring and consultations, lowering barriers for patients in remote areas. These platforms offer patients the advantage of accessing healthcare professionals and resources promptly, regardless of location.
Meanwhile, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) in telemedicine services further enhances diagnostic accuracy and treatment plans. AI technologies can analyse patient data and offer insights that might be missed by traditional methods. This is particularly beneficial for rural healthcare access, where medical expertise might not be immediately available.
Also to discover : Digital nomad apartments: your guide to comfortable remote living
Moreover, modern telemedicine embraces a variety of technologies such as video conferencing tools, electronic health records, and real-time data sharing. These tools collectively ensure a seamless patient experience, enabling healthcare providers to offer comprehensive services.
As the sector evolves, it is crucial to continually assess how these healthcare technology advancements can be harmoniously integrated to cater to the unique needs of rural communities. This ensures a practical, yet progressive, approach to healthcare delivery in less accessible areas.
Have you seen this : Transforming UK Travel Plans: The Power of Augmented Reality for Travel Agencies
Case Studies of Telemedicine in Rural UK
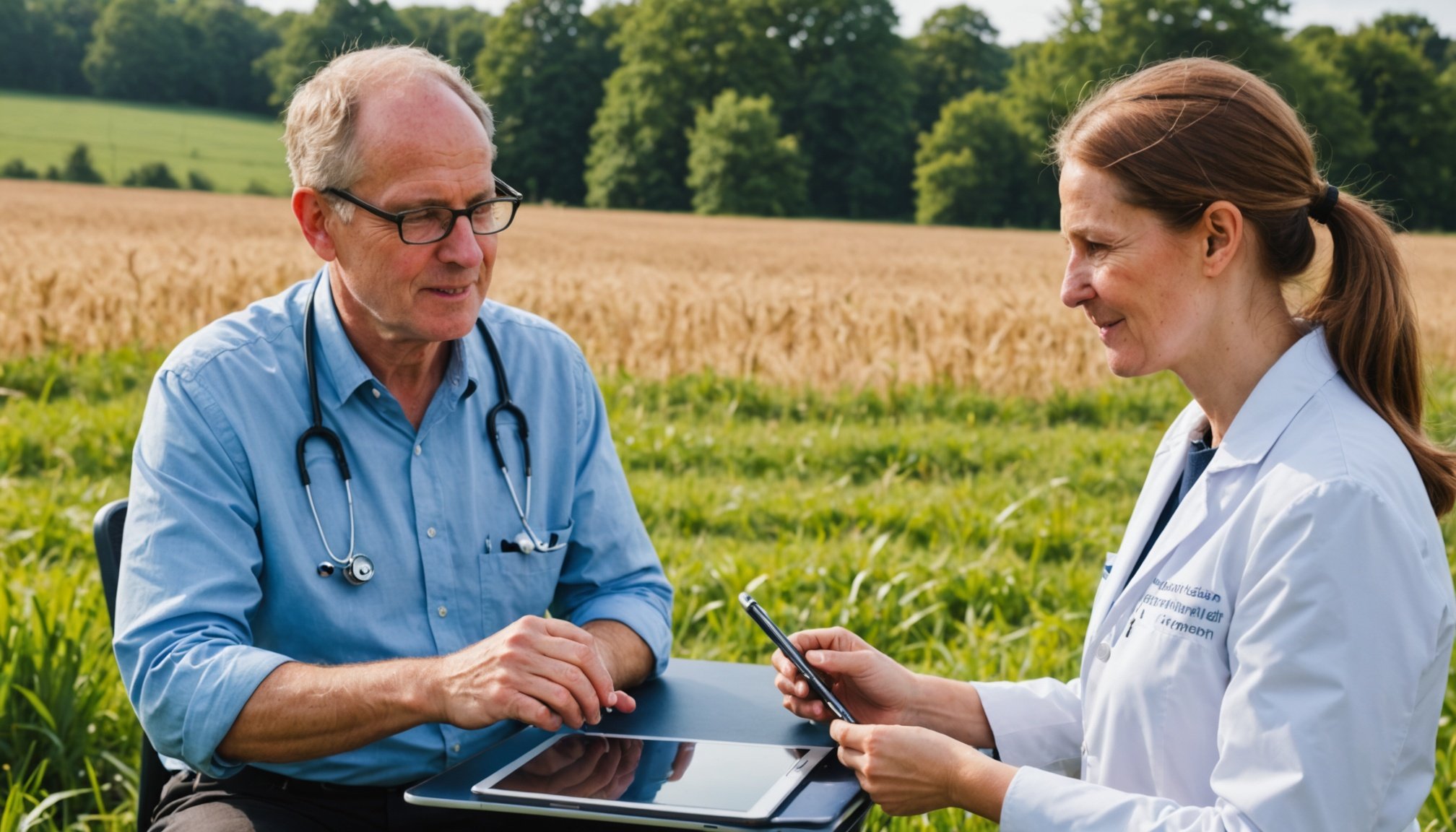
Exploring successful implementations of telemedicine in rural UK offers valuable insights. Telehealth case studies demonstrate the profound impact on patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency. For instance, in the remote areas of Scotland, telemedicine programs have appreciably reduced patient travel time, enhancing access to crucial medical advice. These programs have successfully integrated video consultations and electronic record systems to streamline care delivery.
A standout example is the Welsh Telemedicine Project, which significantly improved diagnostic speed and reduced the hospital admission rate in rural communities. This upstream intervention has led to better health outcomes, fostering a sense of empowerment among patients to actively engage in their health management.
However, these success stories also present lessons that extend beyond regional borders. A common theme is the critical need for reliable internet infrastructure and continuous staff training to operate advanced healthcare technology efficiently. Additionally, collaboration between local health authorities and tech providers is paramount to ensuring long-term sustainability.
These rural healthcare examples underscore the transformative potential of telemedicine when implemented effectively. They highlight the necessity of adapting solutions that are not only technologically viable but also culturally and geographically appropriate, taking into consideration both rural healthcare access and patient preferences.
Benefits and Challenges of Telemedicine in Rural Areas
Telemedicine benefits for rural populations are profound. It fundamentally increases access to healthcare services, allowing individuals in remote locations to connect with specialists without the need for extensive travel. This accessibility significantly improves patient outcomes, offering timely interventions that might otherwise be delayed or unavailable.
However, the implementation of telemedicine solutions is not without its challenges. One major obstacle is the infrastructure requirement, particularly the necessity for reliable internet connectivity to facilitate seamless telehealth interactions. This is a crucial factor that influences both the quality and availability of remote healthcare.
Additionally, there are hurdles related to balancing technological advancements with patient needs. While the innovation itself is vital, it must be user-friendly, ensuring that patients feel comfortable and confident using the technology. Equally important is addressing privacy concerns, as patients must trust how their data is managed and confidentially maintained.
Developing and tailoring rural healthcare solutions necessitates an understanding of the unique cultural and geographical dynamics present in these areas. By carefully considering these factors, telemedicine can be effectively integrated into rural healthcare systems, ultimately improving patient care while addressing current gaps and limitations.
Government Initiatives Supporting Telemedicine
In the United Kingdom, governmental initiatives have become pivotal in advancing telemedicine solutions for rural healthcare. Recognising the potential of telehealth, the government has introduced policies aimed at enhancing rural healthcare access.
Funding is a crucial component, with various grants and resources allocated to support telehealth projects. This financial backing encourages the development of telemedicine infrastructures, ensuring that rural communities receive the necessary tools and technology for effective healthcare delivery.
Furthermore, there is a significant emphasis on collaboration between government bodies and healthcare providers. Such partnerships aim to streamline the implementation of healthcare technology in underserved areas, fostering environments where telemedicine can thrive. These collaborations often involve public-private partnerships, wherein technology companies work closely with healthcare services to tailor solutions that meet the unique needs of rural populations.
Policies also focus on addressing internet connectivity issues, which are often barriers to telehealth services. By improving digital infrastructure, the government helps bridge the gap in healthcare access between urban and rural locations. Through these efforts, the support for telehealth not only enhances patient care but also equips providers with the tools to deliver comprehensive and accessible healthcare services across the rural UK.
Future Trends in Telemedicine for Rural Healthcare
The future of telemedicine in rural healthcare is poised for remarkable transformation as new healthcare innovations take shape. Advancements in AI and machine learning are expected to refine diagnostic processes, offering healthcare providers enhanced tools for accurate decision-making. This technology will likely predict potential health issues by analysing data trends, enabling more proactive care.
Moreover, wearable technology and IoT devices promise to revolutionise how patient data is collected and utilised. These innovations will facilitate continuous monitoring, allowing for real-time health updates and immediate interventions. Imagining a future where patients in remote regions benefit from such sophisticated digital tools is now becoming reality.
Patient engagement is projected to evolve as telehealth platforms introduce more immersive experiences. Virtual reality could provide options for remote physical therapy sessions or mental health consultations, making healthcare delivery more interactive. Such integration will ensure that patients feel more connected and involved in their treatment plans.
However, the adaptability and openness of healthcare providers to these changes will be crucial. Training and development programs will be essential for ensuring that telemedicine advancements are effectively incorporated into rural healthcare ecosystems, thus ensuring seamless transitions and improving patient outcomes.
Patient Experiences with Telemedicine
Small text bridging the headline and the next point.
Testimonials and Surveys
Through telemedicine experiences, patients in rural areas have expressed both satisfaction and concerns about adjusting to new healthcare methods. Surveys and testimonials reveal a positive shift in rural patient care, showcasing how remote consultations have transcended traditional boundaries. For many, the convenience of attending a session from home is invaluable, reducing both time and cost.
Patient Satisfaction and Concerns
While many patients value the accessibility and immediacy of telehealth, some raise concerns about technology reliance and digital literacy. Feedback often points to a need for more intuitive platforms and reliable internet infrastructure to enhance the experience. Patients desire a personal connection, sometimes feeling that technology might hinder traditional doctor-patient interactions.
Recommendations for Improvement
Feedback suggests several ways to improve telehealth services. Enhanced training programs for both patients and staff can bridge digital literacy gaps. Personalised tutorials and step-by-step guides can alleviate anxiety and boost confidence in using telehealth platforms. Patients also recommend improvements in data security and privacy policies to bolster trust. By addressing these areas, telemedicine can refine its role as a cornerstone of rural healthcare.
Steps for Healthcare Providers to Adopt Telemedicine Solutions
Incorporating telemedicine solutions into healthcare services requires a strategic approach to ensure successful transition. For healthcare providers, the journey begins with understanding the telemedicine adoption process and establishing a roadmap tailored to their specific environment.
Essential Steps:
-
Assessment and Planning: Evaluate current infrastructure, identify telehealth needs, and plan solution incorporation. This includes setting objectives, understanding patient demographics, and prioritising technology investments aligned with service capabilities.
-
Training and Support: Comprehensive training for healthcare staff and patients is paramount. Providers must equip their teams with the skills needed to operate telehealth platforms, while offering support programs that guide patients in using these technologies comfortably.
-
Implementing Telehealth Services: Integration should focus on seamless connectivity to current systems, fostering a user-friendly interface that enhances patient care. This involves synchronising electronic health records and ensuring compliance with data protection regulations.
Best Practices:
- Feedback Mechanisms: Regularly gather input from both staff and patients to refine telehealth services.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Engage with technology experts and other healthcare facilities to share insights and resources.
- Continuous Evaluation: Assess telemedicine effectiveness, adapting practices to meet evolving health trends and community needs.